ADVERTISEMENT
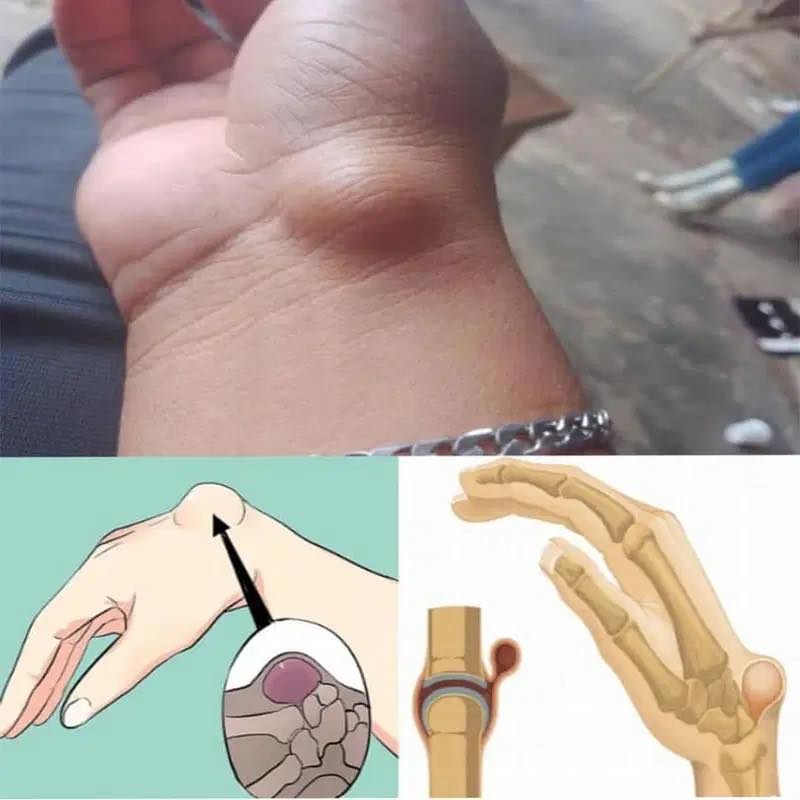
A wrist ganglion cyst, also referred to as a synovial cyst, is a non-cancerous, fluid-filled lump that typically forms on the back or front of the wrist. Although generally harmless, it can sometimes lead to pain, discomfort, or restricted movement. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring effective treatments, individuals can better manage this condition.
What Causes a Wrist Ganglion Cyst?
A wrist ganglion cyst develops when synovial fluid, which normally lubricates joints and tendons, leaks and accumulates into a sac-like structure. While the exact cause is often unclear, several factors may contribute to its formation:
- Repetitive Wrist Strain: Activities that involve frequent wrist movements, such as typing, writing, or playing sports, can increase the risk of cyst development.
- Previous Injuries: A history of wrist sprains, fractures, or trauma may trigger the formation of a ganglion cyst.
- Joint Inflammation: Conditions like osteoarthritis or other forms of joint inflammation can contribute to cyst development.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing ganglion cysts.
Common Symptoms of a Wrist Ganglion Cyst
Wrist ganglion cysts can vary in size and texture, often changing over time. Common symptoms include:
- A visible, soft or firm lump on the wrist, often near a joint or tendon.
- Mild to moderate pain, especially during wrist movement or pressure on the cyst.
- A feeling of pressure, numbness, or tingling if the cyst presses on nearby nerves.
- Reduced wrist mobility or stiffness in more severe cases.
Effective Treatment Options for Wrist Ganglion Cysts
The choice of treatment depends on the cyst’s size, symptoms, and impact on daily activities. Here are the most common approaches:
- Observation (Watch and Wait Approach)
If the cyst is small, painless, and doesn’t interfere with wrist function, doctors may recommend simply monitoring it. In some cases, ganglion cysts resolve on their own without intervention. - Immobilization
Wearing a wrist brace or splint can help reduce pressure on the joint, alleviate discomfort, and prevent the cyst from growing. This approach is particularly useful for cysts caused by repetitive strain. - Aspiration (Fluid Drainage)
A doctor can use a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst, providing temporary relief. However, this method has a high recurrence rate because it doesn’t remove the cyst’s sac. - Surgical Removal (Ganglion Excision)
For persistent or painful cysts that limit wrist function, surgery may be recommended. During the procedure, the entire cyst and its sac are removed, significantly reducing the likelihood of recurrence.
continued on next page
ADVERTISEMENT